What Does Ketamine Do Medically: A Look At Its Healing Potential
Have you ever wondered about certain medications that seem to pop up in unexpected places, offering help in ways we might not initially think? It's almost like some medicines have a secret life beyond their initial purpose. One such substance, ketamine, has really caught the eye of medical professionals for a surprisingly wide range of uses, extending far beyond what many people might typically associate with it. There's a growing buzz about what this particular compound can do when it's put to work in a medical setting, and that, is what we're here to talk about today.
For a long time, ketamine was primarily known for its role in anesthesia, helping people through surgical procedures without feeling pain or being aware. But over the past few years, researchers and doctors have been exploring its unique properties, discovering that it might hold a key to assisting with some truly tough health challenges. This exploration has opened up fresh possibilities, especially in areas where traditional approaches sometimes fall short, offering a bit of hope to those who have struggled to find relief.
So, if you're curious about the different ways this substance is being used to help people feel better, you've come to the right spot. We'll be going through the various medical applications of ketamine, explaining how it works, and discussing who might benefit from it. We'll also touch on what you might expect if you or someone you know considers this kind of treatment, and, in a way, clear up some common questions. We want to give you a clear picture of what ketamine does medically, helping you to understand its place in modern care.
Table of Contents
- A Glimpse into Ketamine's Medical Journey
- How Ketamine Works Inside the Body
- Ketamine for Mental Health Support
- Easing Physical Discomfort: Ketamine's Role in Pain Care
- Other Important Medical Uses
- Receiving Ketamine Treatment: What to Expect
- Important Considerations and Safety
- Frequently Asked Questions About Medical Ketamine
- Looking Ahead: The Future of Ketamine in Medicine
A Glimpse into Ketamine's Medical Journey
Ketamine has quite a history in the world of medicine, first coming into use in the 1960s. For decades, its primary job was to help people go to sleep and stay pain-free during operations. It was valued for its ability to provide a deep state of unconsciousness and pain relief without significantly slowing down breathing or heart function, which, in a way, made it a go-to choice in many surgical settings. This long-standing use as an anesthetic agent is a very important part of its story, setting the stage for everything else that has come after.
From Anesthesia to Broader Applications
As medical science kept moving forward, people started noticing other interesting things ketamine could do. Doctors and researchers observed that patients receiving ketamine for surgery sometimes reported feeling better in their mood afterward, or that their chronic pain seemed to lessen. These observations, you know, sparked curiosity and led to deeper investigations into its effects beyond just making someone unconscious. This curiosity eventually led to exploring its potential for conditions that had nothing to do with surgery at all, opening up entirely new avenues for treatment. It’s a pretty fascinating shift in how a medicine can be viewed and used.
How Ketamine Works Inside the Body
Understanding what ketamine does medically involves looking at how it interacts with our brain and body. It's not a simple one-trick pony; its actions are rather complex and affect several systems. Basically, ketamine works on the nervous system in ways that are quite different from many other medicines we use, which is partly why it offers such unique benefits. It’s a bit like a master key that can open different doors in the brain, leading to various effects.
- Billie Eillish Age
- National Archives Cursive Writing
- Netflix How To Rob A Bank
- Today Show Live Tv
- Who Won Last Year Super Bowl 2024
Affecting Brain Pathways
One of the main things ketamine does is influence the communication pathways in the brain. Think of your brain as a vast network of roads and highways, with signals traveling along them. Ketamine, you see, can change how these signals move, particularly those involved in mood, pain, and thought processes. It helps to create new connections between brain cells, a process that is sometimes referred to as neuroplasticity. This ability to rewire the brain, in a sense, is a big part of why it can have such a profound impact on conditions like depression.
The NMDA Receptor Connection
A very specific target for ketamine is something called the NMDA receptor, which is a kind of protein found on the surface of brain cells. This receptor plays a key role in how brain cells talk to each other, especially when it comes to learning and memory. When ketamine interacts with these NMDA receptors, it changes their activity, leading to a cascade of effects that can quickly improve mood and reduce feelings of pain. This action on the NMDA receptor is considered a primary way ketamine works, and it’s a rather unique mechanism compared to many traditional medications. It’s a bit like adjusting a very important dial in the brain's control room.
Ketamine for Mental Health Support
One of the most talked-about medical uses of ketamine today is its role in helping people with mental health struggles. For individuals who have tried many different treatments without finding relief, ketamine offers a fresh approach. It's not a first-line treatment for everyone, but for those who haven't responded to other methods, it can be a significant step forward. This is especially true for conditions that have proven to be particularly difficult to manage with standard care, so it's a very important option for some.
Helping with Stubborn Depression
For people living with severe depression that hasn't gotten better with typical antidepressants or therapies, ketamine has shown remarkable promise. It can often provide relief much faster than traditional medications, sometimes within hours or days, rather than weeks. This speedy action is a huge benefit, especially for someone who has been struggling for a long time. It works differently from other antidepressants, which is why it can be effective when other things haven't been, basically offering a new pathway to feeling better. Learn more about mental health support on our site.
A Look at Suicidal Thoughts
Perhaps one of the most striking effects of ketamine is its ability to reduce suicidal thoughts very quickly. This can be life-saving in emergency situations where someone is in immediate danger. While it's not a permanent fix, it can provide a crucial window of time for other treatments to start working and for a person to get the support they need. This rapid effect on suicidal ideation is one of the most compelling reasons medical professionals are looking at ketamine, as a matter of fact, as a valuable tool.
What About Anxiety and PTSD?
Beyond depression, researchers are also exploring ketamine's potential for other mental health conditions, including severe anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). While the evidence is still building in these areas, early findings suggest it might help some individuals find relief from overwhelming worry or the lasting effects of trauma. It's a promising area of study, and, you know, the way it works on brain pathways could be beneficial for these conditions too. More research is definitely underway to understand its full scope.
Easing Physical Discomfort: Ketamine's Role in Pain Care
While its mental health applications get a lot of attention, ketamine has a long-standing and important role in managing physical discomfort. It's not just for putting people to sleep during surgery; it can also be a powerful tool for easing pain, especially when other options haven't worked out. This is a crucial aspect of what ketamine does medically, providing comfort when it's most needed. It’s a very versatile compound in that regard.
When Traditional Pain Relievers Fall Short
Sometimes, standard pain medications, like opioids or anti-inflammatory drugs, just don't cut it. For certain types of pain, especially nerve pain or pain that has become chronic and widespread, ketamine can offer a different kind of relief. It works on pain pathways in the brain and spinal cord in a way that can reset how the body experiences discomfort. This makes it a valuable option for people who have struggled to find lasting comfort, providing a new avenue for relief when, frankly, other things have failed.
Addressing Chronic Pain Conditions
Ketamine is being used to help people with various chronic pain conditions, such as complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain. These conditions can be incredibly debilitating and hard to treat. By influencing those brain pathways and reducing the "wind-up" of pain signals, ketamine can sometimes provide a significant reduction in discomfort, allowing people to have a better quality of life. It’s a complex area, but the potential for easing long-term suffering is pretty big, as a matter of fact. link to this page for more insights into managing chronic pain.
Other Important Medical Uses
Beyond its well-known roles in anesthesia, mental health, and chronic pain, ketamine also has a place in other specific medical situations. These uses often involve its quick action and its ability to provide a safe level of sedation and pain control. It’s a rather useful tool for doctors in certain urgent or procedural settings, demonstrating its wide range of applications. It's not just a one-trick pony, you know, it has several different applications.
Emergency Situations
In emergency rooms, ketamine is sometimes used to sedate patients who are agitated or experiencing severe pain, especially when other medications might not be suitable. Its rapid onset and relatively stable effect on breathing and blood pressure make it a good choice for quickly getting a situation under control. For instance, if someone has a dislocated joint that needs to be put back in place, ketamine can provide the necessary sedation and pain relief quickly, allowing the medical team to perform the procedure effectively. It's a very practical solution in high-pressure moments.
Procedural Sedation
Ketamine is also used for procedural sedation outside of major surgery. This means it can help patients relax and feel no pain during shorter, less invasive medical procedures, like setting a broken bone, changing a painful dressing, or performing certain diagnostic tests. It allows the procedure to happen smoothly while keeping the patient comfortable and safe. The ability to provide effective sedation without completely suppressing breathing is a major advantage here, making it a valuable option for various medical interventions, so it’s pretty useful.
Receiving Ketamine Treatment: What to Expect
If you or someone you know is considering ketamine treatment for a medical condition, it's natural to wonder what the experience might be like. It's not something you take home and use on your own; medical ketamine is always administered under careful supervision in a controlled setting. This supervision is very important to ensure safety and effectiveness, and, you know, to manage any immediate effects. It's a procedure that requires a team of professionals.
Different Ways It's Given
Ketamine can be given in several ways, depending on the condition being treated and the specific medical setting. For depression or chronic pain, it's often given intravenously (IV infusion), meaning it goes directly into a vein over a period of time. There are also nasal sprays and oral forms that might be used, particularly for maintenance doses or for specific conditions. The method chosen will depend on what the doctor thinks is best for your particular situation, so, basically, it's a personalized approach.
The Treatment Environment
When you receive ketamine, you'll typically be in a calm, quiet medical environment, like a clinic or hospital room. Medical staff will monitor your vital signs, such as your heart rate and blood pressure, throughout the treatment. The goal is to make you feel as comfortable and safe as possible during the experience. This careful monitoring is a very important part of the process, ensuring everything goes smoothly, and, you know, that any immediate reactions are handled right away.
Possible Sensations and Effects
During the treatment, people often report feeling a sense of detachment or a dream-like state. Some describe it as a floating sensation, or a feeling of being outside their body. These effects usually last for a short period, often less than an hour, depending on the dose and how it's given. It's important to remember that these sensations are a normal part of the ketamine experience, and they typically fade away as the medication leaves your system. You might feel a little groggy or lightheaded afterward, but that usually passes quickly too, so, in some respects, it’s a temporary feeling.
Important Considerations and Safety
While ketamine offers significant medical benefits, it's crucial to approach its use with a full understanding of the important considerations and safety measures. It's a powerful medication, and like all powerful medications, it comes with potential risks. This is why it is only used under strict medical guidance, as a matter of fact, to ensure that the benefits outweigh any possible downsides. Safety is, very, very important.
Potential Side Effects
Some people might experience side effects during or after ketamine treatment. These can include a temporary rise in blood pressure or heart rate, nausea, dizziness, or confusion. Less common but more serious effects can occur, which is why close monitoring by medical professionals is absolutely necessary. It's important to discuss any concerns you have with your doctor before starting treatment, and, basically, to report any unusual feelings during or after the session. They can help you understand what to expect and how to manage any discomfort.
Who Should Not Use It
Ketamine is not suitable for everyone. People with certain medical conditions, such as uncontrolled high blood pressure, heart problems, or a history of psychosis, might not be good candidates for ketamine treatment. Your doctor will conduct a thorough evaluation to determine if ketamine is a safe and appropriate option for you. This careful screening process is a very important step to protect your well-being, you know, ensuring that the treatment is right for your specific health picture.
The Need for Medical Supervision
Because of its effects and the need for careful dosing, ketamine should only be administered by trained medical professionals in a supervised setting. Self-administering ketamine or using it outside of a legitimate medical context can be very dangerous and lead to serious health consequences. This is not a medicine to experiment with on your own; it requires expert oversight to be used safely and effectively. It’s a pretty serious medication, and, you know, needs to be handled with extreme care.
Frequently Asked Questions About Medical Ketamine
People often have a lot of questions when they first hear about ketamine's medical uses. Let's tackle some of the common ones that people often ask, helping to clear up any confusion and provide a bit more clarity. These questions are, you know, pretty common, and it's good to get some straightforward answers.
Is ketamine a painkiller?
Yes, ketamine does have pain-relieving properties. While it's perhaps more widely known for its use in anesthesia, it's also a very effective painkiller, especially for certain types of chronic pain that don't respond well to other medications. It works on different pain pathways in the brain and spinal cord compared to traditional painkillers, which is why it can be helpful when other options haven't worked. So, in a way, it definitely acts as a pain reliever.
What is ketamine used for in hospitals?
In hospitals, ketamine is used for a variety of purposes. Its primary use is as an anesthetic for surgical procedures, helping patients remain unconscious and pain-free. It's also employed for procedural sedation during shorter medical interventions, like setting bones or wound care. Beyond that, it's increasingly used to help people with severe, treatment-resistant depression, and sometimes for managing acute or chronic pain that has been difficult to control. So, basically, its hospital uses are quite varied, from the operating room to psychiatric care.
How long do the effects of ketamine last?
The immediate effects of ketamine, particularly the dissociative or dream-like sensations, usually last for a relatively short period, often around 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the dose and how it's given. However, the therapeutic benefits, especially for mood improvement in depression, can last much longer, sometimes for days or even weeks after a single treatment. This longer-lasting benefit is what makes it so appealing for mental health care, as a matter of fact, even if the immediate sensations are brief. You might feel a little tired or "off" for a few hours afterward, but the main sensations fade quickly.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Ketamine in Medicine
The medical community continues to explore the full potential of ketamine. Research is ongoing to better understand its mechanisms, refine treatment protocols, and identify even more conditions it might help with. As we learn more, it's possible that ketamine will become an even more integrated part of care for a wider range of patients. This ongoing discovery is a very exciting part of medicine, you know, always looking for better ways to help people. It’s a pretty hopeful time for those who have been struggling to find effective treatments.
New forms of delivery and combinations with other therapies are also being investigated, aiming to make treatments more accessible and effective. The conversation around ketamine is certainly growing, and it's clear that this medication has a significant and evolving role to play in modern healthcare. The future looks rather promising for this versatile compound, and, you know, it’s a testament to how medical science keeps pushing boundaries to find solutions for complex health issues. You can find more information about ketamine's medical uses from reliable sources.
Understanding what ketamine does medically is about recognizing its unique place as a powerful tool in the hands of trained professionals. It offers hope for those facing tough health battles, from persistent mood challenges to stubborn pain. If you're curious about whether ketamine treatment might be an option for you, it's really important to have a conversation with a trusted medical doctor. They can provide personalized advice and help you figure out the best path forward for your health journey, so, basically, talking to an expert is the most important step.

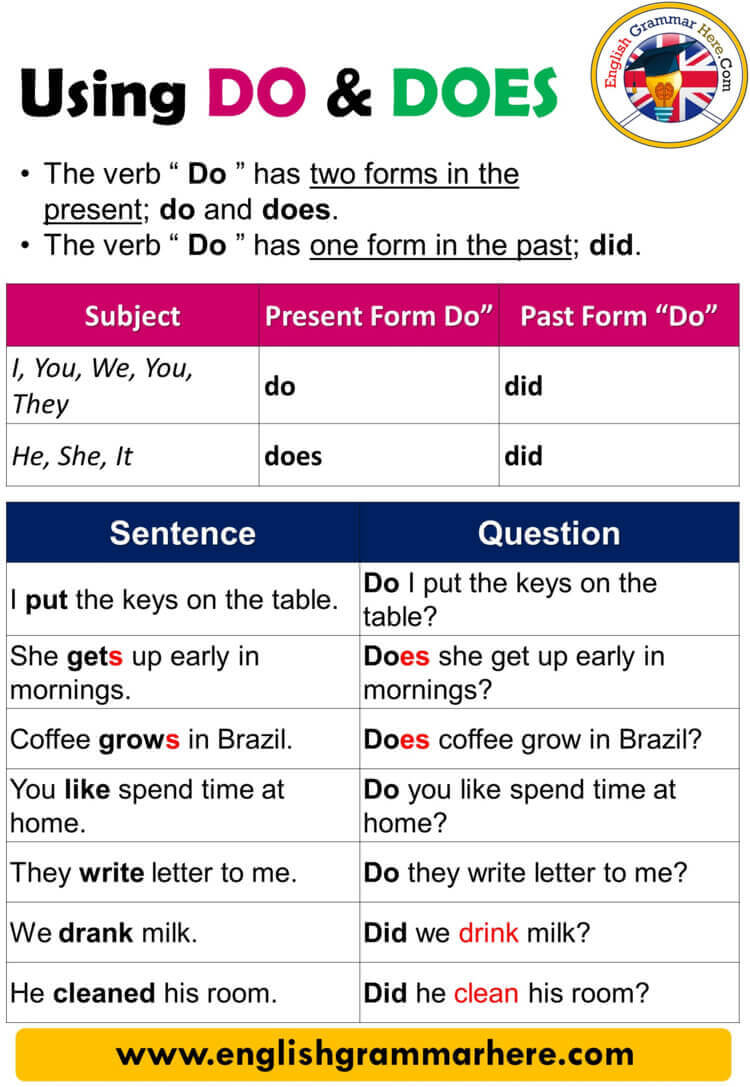

Detail Author 👤:
- Name : Karlee Zieme
- Username : jodie.hintz
- Email : rowena.bartoletti@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 2007-01-17
- Address : 5463 Barton Ridges Suite 344 New Elda, IA 25396-8956
- Phone : 352-640-2247
- Company : Weber-Daniel
- Job : Alteration Tailor
- Bio : Amet dolor sit rerum doloremque excepturi magni. Recusandae enim officiis similique et accusamus accusamus. Fugiat minus assumenda ut et. Repudiandae sed sed nemo id qui ut.
Socials 🌐
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/shanna.emard
- username : shanna.emard
- bio : Animi rem nisi perspiciatis expedita atque minima. Facilis magnam enim doloremque aperiam sed. Provident perspiciatis nemo magnam pariatur.
- followers : 1881
- following : 753
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/shanna_emard
- username : shanna_emard
- bio : Expedita maiores repudiandae et magnam. Provident eius eos labore sed culpa aliquam non amet.
- followers : 544
- following : 235